
So the total number of g moles of gas present = (1-α) + nα or 1 + (n-1)α. One molecule of substance A splits up into n molecules of B by specific heat A > nB.Īt equilibrium for each g mole of A will be (1 – α) g moles of undissociated A and nα g moles of B. The total number of moles that suffer dissociation calculates the degree of dissociation. The mass remains the same thus, D* decreases.
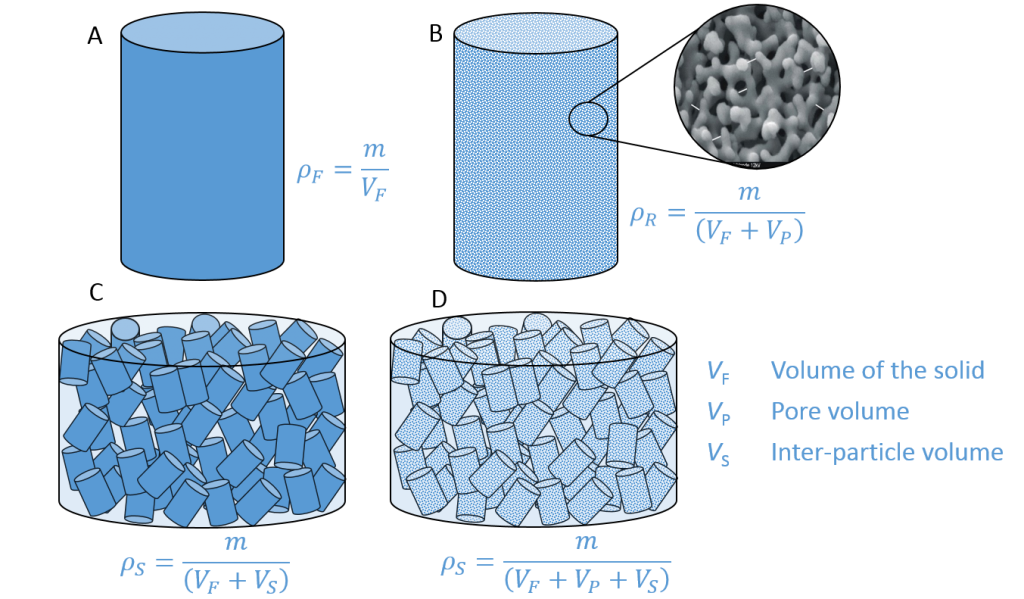
This is caused due to thermal bond dissociation.Īt the constant pressure because of the dissociation, the volume of the gases increases with the increase of the mole number. Only at a high temp this phenomenon called abnormal densities. Vapour density (Symbol V.D) = mass of n molecules of gas/mass of n molecules of hydrogenĬertain chemical substances, like ammonium chloride, hydrogen peroxide, etc., have their calculated vapor densities less than the theoretical measurements. It may be defined as the mass of a certain volume of a substance divided by the mass of the same volume of hydrogen. It is defined as the ratio of gaseous substance and hydrogen density under the same temperature and pressure. The relation between pressure and density is expressed through the equation of states for ideal gases by applying Boyle’s and Charles and Gay-lussac law. The air is heated until the balloon’s total density is less than the atmosphere. Even in hot air balloons, the air becomes less dense when heated. One of the many uses of density is to calculate the density of the substance to determine if it will float on another. It is the density of gas when the ratio of density per unit pressure is extrapolated to zero pressure.ĭensities are critical for many uses. Limiting densities are densities that are calculated from the above gas equation and are only approximate and inaccurate. The density version of the ideal gas law is PM = dRT, where P is pressure measured in atmospheres (atm), T is temperature measured in kelvin (K), R is the ideal gas law constant 0.0821, but M is now the molar mass (g/mole), and density (g/L) symbol is denoted as d.īy rearranging the formula to PM/RT = d, the units of atm, mol, and K will cancel, and the value will be left with the g/L units for density. Therefore, Ideal gas equations are not accurate. It gives the approximate value under average temperature and pressure. The ideal gas law formula calculates ideal gases’ molar mass and density. The normal density calculators use 0 degrees C and one atmospheric pressure. Freshwater has about 1.0 g/cm3, rocks around 3g/cm^3, and metals have densities above 6 g/cm^3. Question: What is the density of a cube of sugar weighing 11.2grams measuring 2 cm on a side?ĭensity (symbol D)= mass/volume D= 11.2 grams/8 cm3 D = 1.4 grams/cm3ĭensities for gases are on the thousandths of grams per cubic centimeter liquids have densities of 1.0g/cm^3. The formula used to calculate the density is If you want to know the density of a material, you will have to weigh it and then measure it with volume. Calculating Densityĭensity cannot be measured directly. Different materials with different masses have different densities for the same volume. In a qualitative type, it shows the heaviness of an object at a constant volume. The liter and tonne are not part of SI but are used with density. Generally, the density of water is taken as the standard value, which is the SI unit of density: Therefore, we consider the size and volume of the object. A huge sponge may weigh a lot, but its density is low because it weighs a minimal per unit of its volume. Familiar words like ‘heavy’ or ‘light’ refer to mass, not density. People often get confused between mass and density. In chemistry or physics, density is expressed by the symbol ρ or D, and the mathematical expression is p=m/v that is, density symbol p is equal to the total mass (M) divided by total volume (v). It is widely used to identify the pure substance and to estimate the composition of different kinds of a mixture it can be used to define the substance.

For example, osmium is the densest element known under standard conditions. Different materials exhibit different densities. It indicates how much of a substance occupies a specific volume at a defined temperature and pressure. Density is the mass of a substance divided by its volume.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
